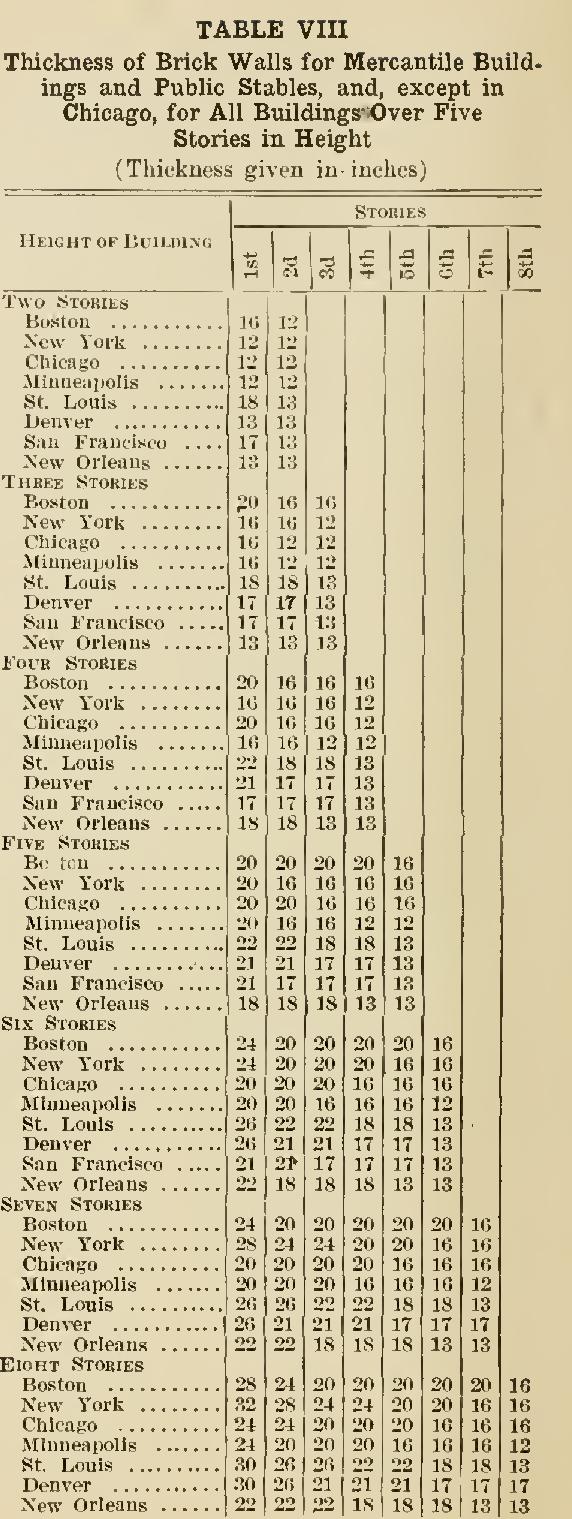
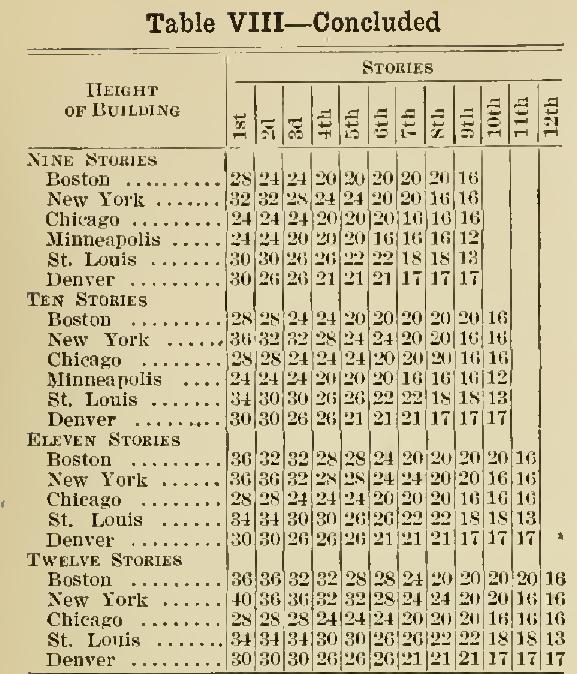
New York Building Code - Brick Building Practice
bricks and wall
Table IX may be taken as a guide to the proper thickness, at the different stories, for residence walls of varying height and length.
The sizes for brick adopted by the National Brickmakers' Association in 1899 were as follows: Common brick 81/4 x 4 x in, Face brick 8% x 4 x 2% in.
Paving brick 81/2 x 4 x 2% in.
Roman brick 12 x 4 x 11/2 in.
Fire-clay brick 9 x 41/2 x in, All bricks should be sorted into different thicknesses for first-class work.
The weight of brick varies with the make and size. A common brick will weigh from 4 to pounds, while pressed brick weigh from 5 to pounds. Paving bricks weigh from 6 to 7 pounds each; and fire-clay bricks, about 7 pounds each.

Weight of Brickwork. The weight of brickwork per cubic foot varies both with the quality of brick and with the thickness of mortar joints. A fair average value for common bricks laid in lime mortar is about 120 pounds per cubic foot. When laid in cement mortar, a cubic foot of common brickwork weighs about 130 pounds. Paving brick weighs about 160 pounds per cubic foot.
Some authorities consider that 112 pounds per cubic foot is plenty to allow for the weight of brickwork; and it is often stated upon that basis, that the weights of brickwork per square foot of wall surface for different thicknesses of wall are as given on page 38. The terms "9-inch wall," "13-ineh wall," etc., may be used in some localities as flinch wall, 12-ineh wall, etc., figuring the wall thickness as if made up of whole bricks and half-bricks.
In laying of brickwork, the lower bricks are subjected to the weight of all brickwork above the lower courses, together with weights of roof, floors, etc., and should be figured to see if their strength is sufficient to carry these pressures. Common brick in lime mortar will hold about 100 lbs. per square inch; when laid in cement mortar, about 150 lbs. per square inch. Hard-burnt and paving bricks laid in cement mortar will bold about 200 to 250 lbs. per square inch.
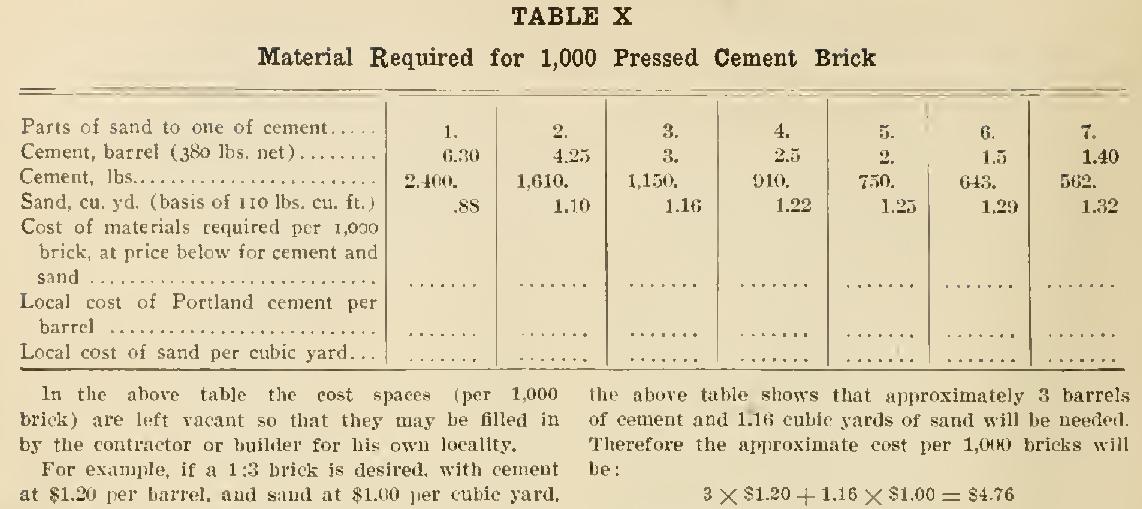
Pressed Cement Brick Table X will be found useful in estimating the quantities and cost of materials required for the manufacture of pressed cement brick.
Labor in Laying Brickwork Since the price of labor and the length of working clay vary so greatly in different parts of the country, no attempt will be made to give absolute prices for labor in laying brickwork. Instead of actual figures, there will be given the number of bricks that an average workman should be able to lay in a given length of time on a stated class of work. Knowing local rates of wages and hours in a working day, the contractor should be able to judge with a fair degree of correctness as to the probable cost of the work in hand.
In wall construction, there are generally allowed from 1 to laborers for each brickmason. These men provide the mason with all necessary material, and leave it in a place convenient for use. The wages of these laboring men, added to the wages of the brickmasons, and divided by the number of thousand brick laid in the wall in a (lay, would give the cost of laying per thousand.
The following list of different types of work, indicating the actual number of bricks that can fairly be expected to be laid per clay by the average workman, will be of service in estimating. An average man will lay: 1,200 bricks in plain wall in 8-hour day. 2,000 bricks in heavy work in 8-hour day. 1,800 bricks in arches in 9-hour day. 3.500 bricks in sewers in 8-hoar day. 7,000 bricks in pavements in 10-hour day. 600 bricks in small chimneys in 0-hour day. 450 bricks in pressed work in 8-hour day. 400 bricks in veneer work in 8-hour day.