Ipecacuanha
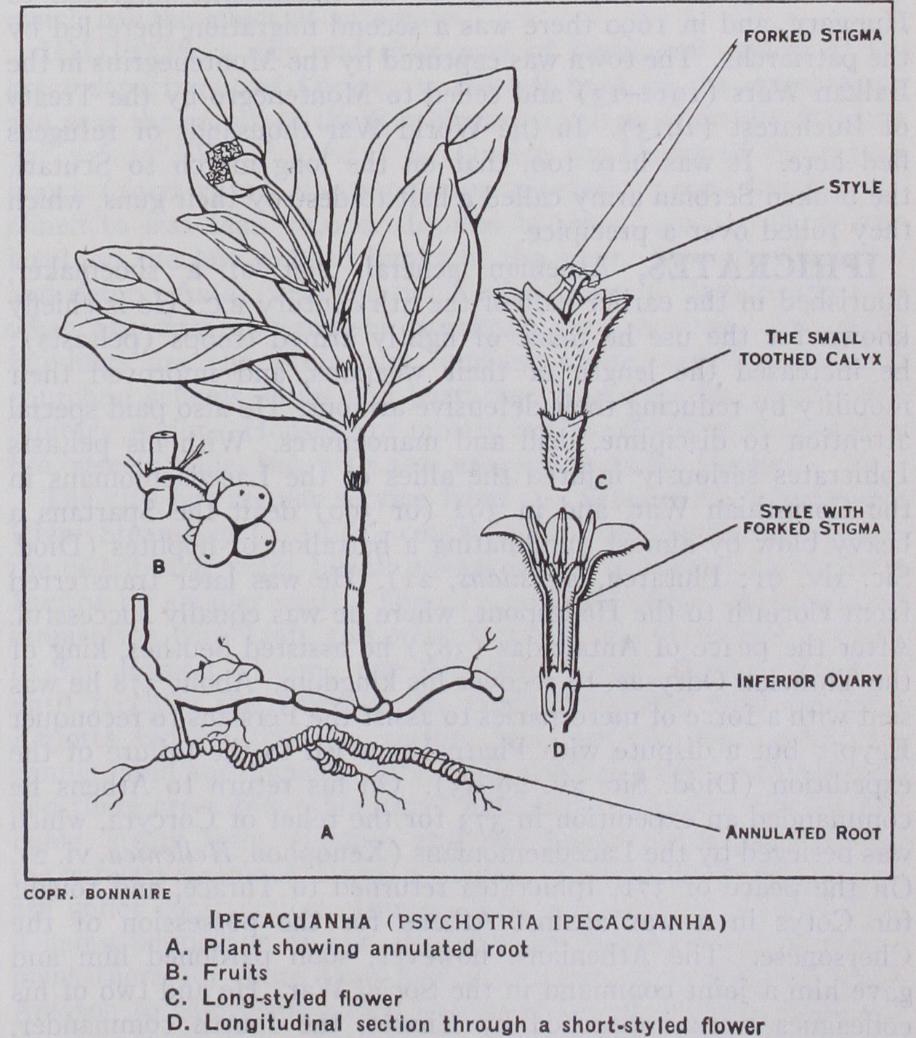
IPECACUANHA. The root used in medicine under this name is obtained from Psychotria (or Uragoga) Ipecacuanha, a rather small shrubby plant of the family Rubiaceae. It is a native of Brazil, growing in clumps or patches in moist shady forests from 8° to S., and is also found in Colombia and probably in Bolivia. The great value of the drug in dysentery led to attempts to acclimatize the plant in India. Like other dimorphic plants, ipecacuanha ripens seeds best when cross-fertilized, and presents various forms.
Ipecacuanha root occurs in pieces about two or three lines in thickness, of a greyish-brown or reddish-brown tint externally, having a ringed or annulated surface (see illustration), and exhibit ing a white or greyish interior and a hard wiry centre. It has a faint rather musty odour and a bitterish taste. The variety im ported from Colombia and known as Cartagena ipecacuanha differs only in its larger size and in being less conspicuously annulated. Ipecacuanha owes its properties to the presence of rather more than 1% of the alkaloid emetine, which occurs only in the cortical portion of the root. It is a white amorphous substance, with the formula It has a bitter taste, no odour, and turns yellow when exposed to air and light. There are also present a volatile oil, starch, gum and a glucoside, which is a modifica tion of tannin and is known as ipecacuanhic acid. The dose of the powdered root is a to 2 grains when an expectorant action is desired, and from 15 to 3o grains when it is given as an emetic, which is one of its most valuable functions.
Ipecacuanha powder is a powerful cutaneous irritant, even causing pustulation. When inhaled it causes violent sneezing and a mild inflammation of the nasal mucous membrane, resembling a common cold in the head. Small doses stimulate the secretions of the mouth, stomach, intestine and liver. The drug, therefore, increases appetite and aids digestion. Toxic doses cause gastro enteritis, cardiac failure, dilatation of the blood-vessels, severe bronchitis and pulmonary inflammation closely resembling that seen in ordinary lobar pneumonia. In this respect and in its action on the skin, the drug resembles tartar emetic. Ipecacuanha is very frequently used as an expectorant in cases in which the bronchial secretion is deficient. Its diaphoretic properties are employed in the pulvis ipecacuanhae composites or Dover's pow der, which contains one part of ipecacuanha powder and one part of opium in ten.
Other plants to which the name of ipecacuanha has been popu larly applied are American ipecacuanha (Gillenia stipulacea), wild ipecacuanha (Euphorbia Ipecacuanha), bastard ipecacuanha (Asclepias curassavica), Guiana ipecacuanha (Boerhavia decum bens), Venezuela ipecacuanha (Sarcostemma glaucum), and ipe cacuanha des Allemands (Vincetoxicum officinale). All these possess emetic properties to a greater or less degree.