Flame
FLAME) .
12. Retort stand with rings, clamps, and bosses.
13. Still (with constant-level device) and condenser.
14. Drying tower. Similar in function to 16, but used where gases have to be passed through solids.
15. Aspirator. If this is filled with water, and the stopper is replaced by a cork carrying a tube, on opening the tap water will flow out, and this will draw air through the tube, which may be attached to any other apparatus.
16. Wash-bottle for gases (Drechsel pattern) . If the gas is bub bled through the liquid it can be freed from one or more impurities, e.g., it can be dried by passage through concentrated sulphuric acid, or freed from carbon dioxide by a solution of caustic potash.
17. Kipp's apparatus. Hydrochloric acid (HCI) is allowed to run down the central tube and rise so as to act on the iron sulphide; if the tap is open, sulphuretted hydrogen (H2S) is expelled by the "head" of acid ; when the tap is shut, the gas forces the acid into the top bulb and no more gas is produced. If marble is used instead of iron sulphide, carbon dioxide (CO2) is obtained.
18. Desiccator. Strong sulphuric acid or granular calcium chloride is kept in the bottom ; the material to be dried is spread on a watch-glass or clock-glass resting on the gauze. If the nozzle is attached to a pump, the vacuum produced accelerates drying.
General Apparatus—continued.
19. Separating funnels: (a) pear-shaped—also called a dropping funnel ; and (b) cylindrical. If ether has been used to extract an organic substance from water, two layers are formed and the lower (aqueous) layer can be run off. Similarly, if chloroform had been used instead of ether, the lower layer would be the chloroform extract.
zo. Pestle and mortar (of porcelain).
21.
Foot blow-pipe.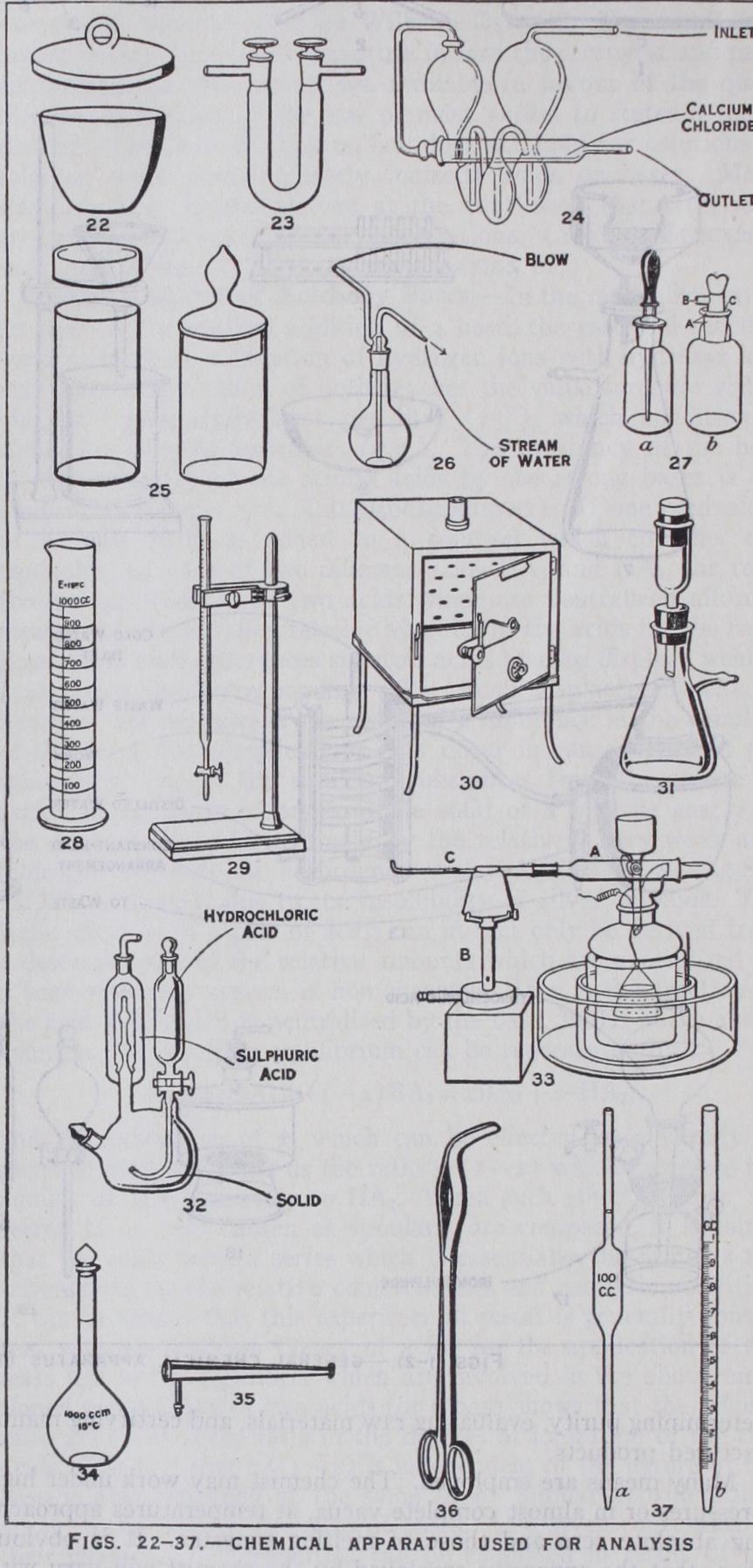
Apparatus used in Analysis.
22. Crucible and lid; used for igniting precipitates.
23. U-tube. May be filled with granulated soda-lime to absorb carbon dioxide, or with pumice soaked in sulphuric acid to absorb water vapour. The ground-in taps can be turned to shut off connection with the outer air.
24. Potash bulbs. A 50% aqueous solution of potash is in the bulbs. A gas has to bubble through the three in succession and is dried in the calcium chloride tube ; the increase in weight, if any, is due to carbon dioxide absorbed from the gas.
25. Weighing bottles, for protecting material from the air while it is being weighed. A portion of the contained substance is tipped out and the whole reweighed, the amount of material thus taken being the difference in weight.
26. Wash bottle. A fine stream of water (or other
liquid) can be directed where required.27. Dropping-bottles: (a) By slightly pressing the rubber teat and releasing the pressure, a few drops are drawn up in the teat and can be squeezed out one at a time when the nozzle is withdrawn. (b) Liquid flows along the capillary tube at A when the bottle is tilted, and a drop falls from B, air entering through another channel at C. Used chiefly for indicators (q.v.).
28. Measuring cylinder. Used for rough measurements of vol umes of liquids.
29. Burette in stand. Used for titrations. The graduated scale shows what volume of liquid is delivered (see
