Worsted Manufacture
flyer, bobbin, yarn, spindle, rollers, usually, front, wools and swift
Spinning.
The flyer spinning frame is very similar to the drawing frame, consist ing of back rollers, carriers and front rollers, with the necessary spindle and flyer to put twist into the yarn and to wind it upon the bobbin. From the two-spindle gill-box to the spinning frame the spindle, bobbin and flyer combination is employed with the ob ject just mentioned. From fig. 5 the action of this combination will be clearly under stood. Drafting takes place as usual be tween the back and front rollers, the car riers controlling the sliver between the two. On emerging from the front rollers the yarn usually passes through an eyelet to centre it over the centre of the spindle; it then takes a turn or two round the flyer leg, through the twizzle or eyelet on the flyer and on to the bobbin F. The flyer may be freely rotated by means of the wharl J and through the spindle G upon the top of which it is screwed. The bobbin fits loosely over the spindle and rests lightly upon the lifter; this latter, being controlled by the lifter mechanism, slowly raises and lowers the bobbin during the "spin" past the fixed plane of delivery of the yarn, i.e., the eyelet of the revolving flyer. Now, if for one moment it be considered that the bobbin may not revolve on the spindle but may be slid up and down by the lifter motion, then, if the front rollers deliver the necessary yarn, the flyer will wrap it in successive layers upon the bobbin—but no twist will be inserted.
On the other hand, if the bobbin is perfectly free upon the spindle and the front rollers cease delivering yarn, then the flyer, by means of the yarn, will pull the bobbin round at the same speed as it goes itself, and the yarn will be twisted but not wound upon the bobbin. By ob taining an action in between these two extremes both twisting and winding on to the bobbin is effected. The speed of the bobbin is suitably retarded by washers placed between it and the lifter plate, so that it just drags suffi ciently to wind up the yarn "paid out" by the front rollers. The turns per inch are in proportion to the yarn delivered and the rev olutions of the flyer. Thus if, while r in. of yarn is delivered, the flyer revolves twelve times the turns per inch will be ap proximately twelve. This is the theory of the spindle, flyer and bobbin action.
Preparing Short Wools.— Wools not more than 7 in. long are usually prepared for combing by the operation of carding. On first thought it might be imagined that carding would result in broken fibres and a poor yield of top. That this is not so is evident from the fact that there is a ten dency to card wools from 7 to io in. long, this tendency being due to the relative cheapness of carding as compared with pre paring. If long wools were fed
directly on to a swift, no doubt serious breakage of fibre would occur, but it is customary to place before the first swift of a worsted card a series of four opening rollers and dividers—with their accompanying "burring rollers"—to open out the wool grad ually, so that when it eventually reaches the first swift it is so opened out that further opening out instead of breakage occurs. Some carders use a breast of small swift in place of these open ing rollers--mostly on account of economy. The swift is usually surmounted with four workers and strippers and is very similar to the woollen carder, save that the workers and doffer are larger, thereby effecting more of a combing action and working econom ically by reason of the greater wearing surface brought into play. As botany wool is usually brought directly from the wash bowl to the feed sheet of the card, it is usual to clothe the first cylinders with galvanized wire clothing.
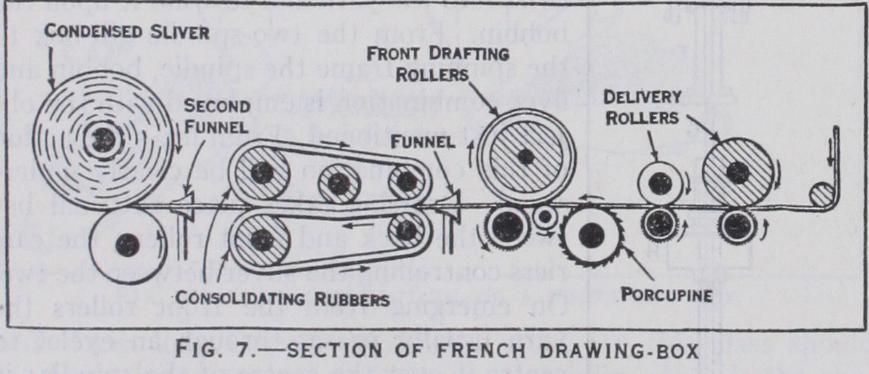
After the carding the wool is back-washed and gilled—on simi lar lines to English wool—and then is ready for combing. After combing, the tops are "finished" by being passed through two finisher-boxes, the last of which "balls" the tops for market.
Short wools are drawn and spun on very similar lines to the longer wools, save that the boxes are more in number and are in some cases lighter in build. The boxes usually employed in a botany set are as follows : two double-head can gill-boxes, two two-spindle gill-boxes, a four-spindle drawing-box, a six-spindle weigh-box, an eight-spindle drawing-box, two eight-spindle finish ing-boxes, two twenty-f our-spin dle second finishers, three thirty two-spindle dandy reducers, ten thirty-two-spindle dandy rovers, with ten two-hundred-spindle cap spinners to follow.
The doublings as a rule are about 7, 6, 6, 6, 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 2 and the drafts 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8 at the respective boxes, an endeavour as a rule being made to obtain a roving of which 4o yds. = 2 drams, as this is the most convenient size for being spun into fine botany count of yarn.
Following the lead of the cot ton trade endeavours have been made to control the driving and speed of both flyer and bobbin in all the drawing frames of such sets as that described above. Such control is usually effected by a pair of cones, from which this system has taken its name, viz., "cone" drawing. The chief advantages of this system seem to be the possibilities of employ ing larger bobbins, and thus obtaining greater production, the con sumption of relatively less power, and more particularly the pro duction of a softer sliver with less twist, partaking more of the character of a French roving.